Thirty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-24)
[Paper], [Code]
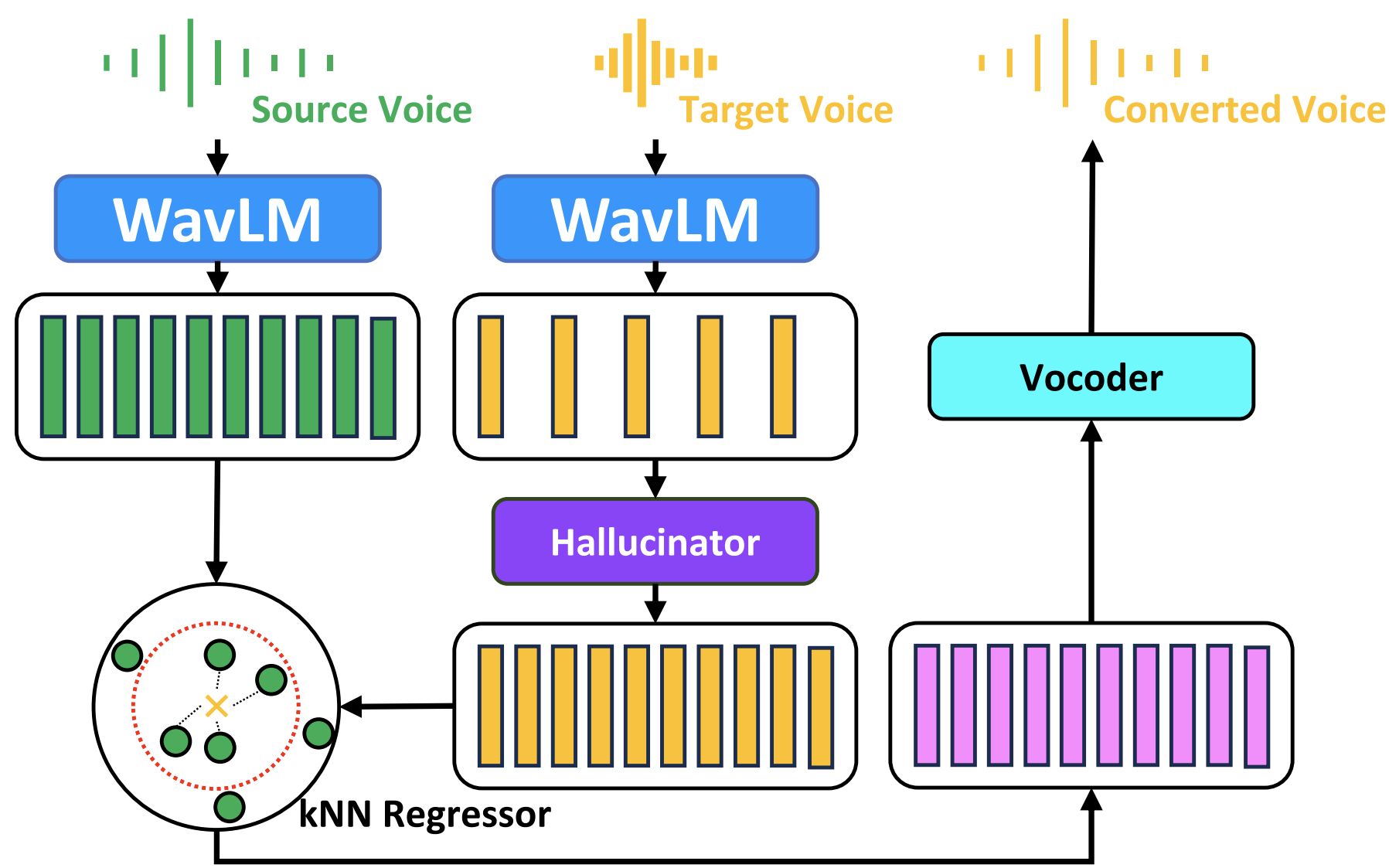
This section compares Phoneme Hallucinator with several strong baselines such as VQMIVC, YourTTS, kNN-VC and FreeVC.
| Source | Target | VQVIMC | YourTTS | kNN-VC | FreeVC | Phoneme Hallucinator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This section conduct ablation studies of the impact of target audio length on the converesion. Specifically, we show the conversion results using the first 1s, 3s, 5s, 7s and 9s of the target audio respectively.
| Source | Target | VC Results (1s) | VC Results (3s) | VC Results (5s) | VC Results (7s) | VC Results (9s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This section conduct ablation studies of the number of hallucinated features ranging from 5,000 to 50,000.
| Source | Target | VC Results (5,000) | VC Results (15,000) | VC Results (30,000) | VC Results (50,000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This section conduct ablation studies of the model architecture. MOD denotes the modulation mechanism, CAT denotes the concatenation mechanism and PEQ denotes the permutation equivariant embedding.
| Source | Target | Full model | w/o MOD | w/o CAT | w/o PEQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This section shows cross-lingual voice conversion results. Note that our phoneme hallucinator is trained on English data only.
| Source | Target | kNN-VC | Phoneme Hallucinator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | Spanish | ||
| Chinese | Spanish |